Discover the difference between benign and malignant tumors, warning signs you can’t ignore, and breakthrough treatments. Learn how to reduce your risk today.
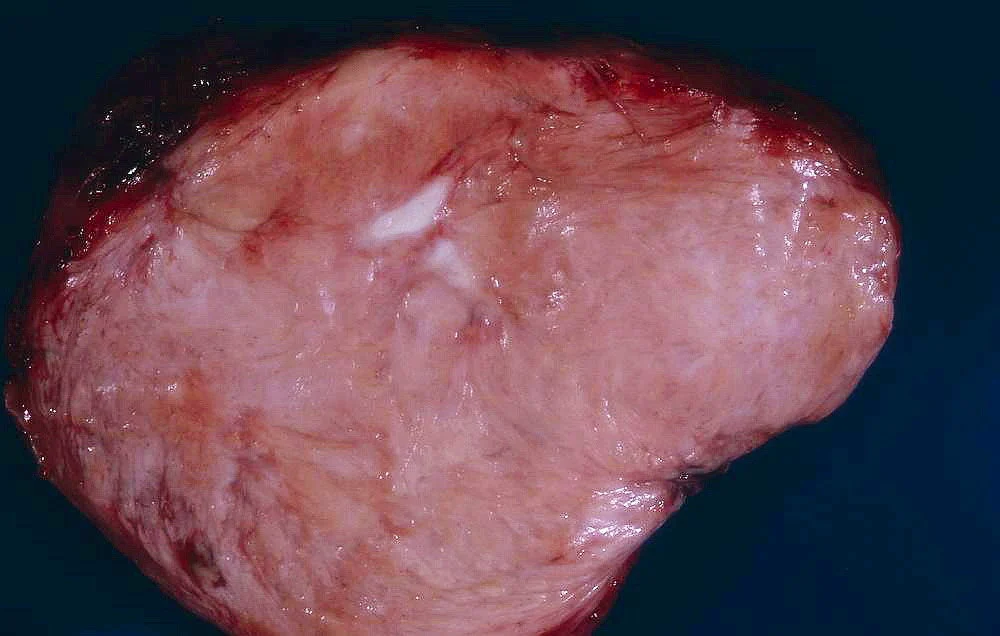
What Is a Tumor?
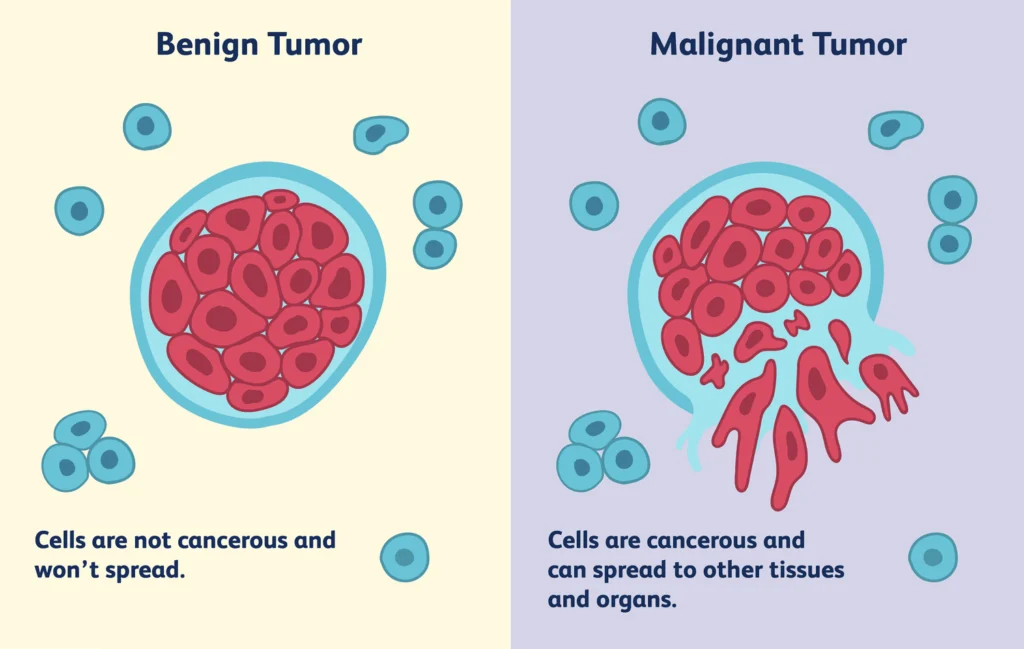
A tumor is an abnormal mass of tissue that forms when cells divide uncontrollably. While often linked to cancer, not all tumors are cancerous:
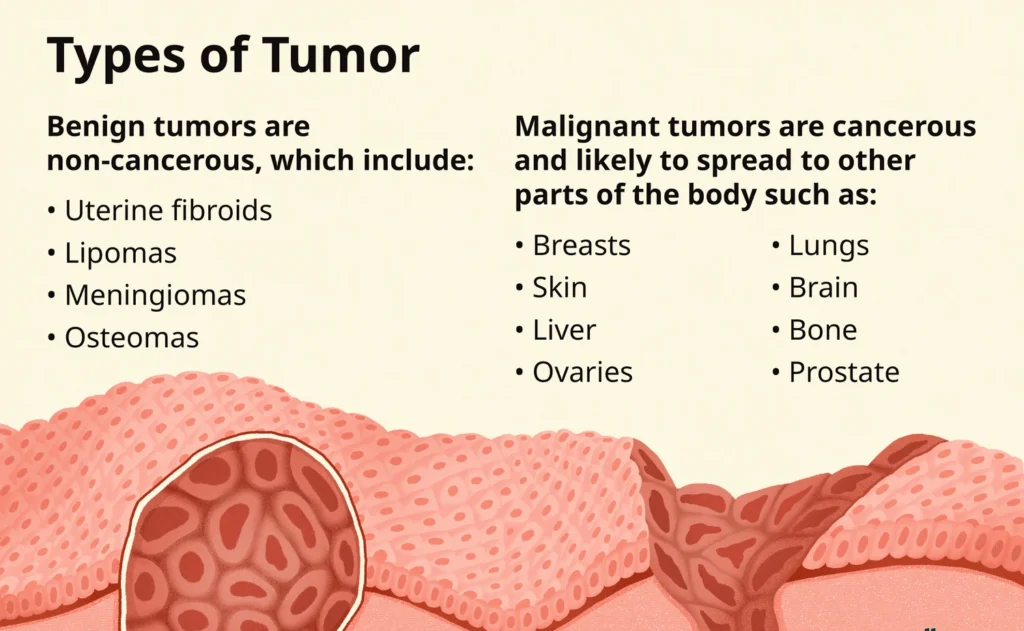
- Benign Tumors: Non-cancerous, slow-growing, and rarely life-threatening (e.g., lipomas, uterine fibroids).
- Malignant Tumors: Cancerous, invasive, and can spread (metastasize) to other organs.
Key Stat: 1 in 3 people will develop a tumor in their lifetime, but only 40% of tumors are malignant.
Types of Tumors: Benign vs. Malignant

| Benign Tumors | Malignant Tumors |
|---|---|
| Lipomas (fatty tissue) | Carcinomas (skin, organs) |
| Meningiomas (brain) | Sarcomas (bone, muscle) |
| Adenomas (glandular tissue) | Leukemias (blood/bone marrow) |
| Osteochondromas (bone) | Lymphomas (immune system) |
Note: Pre-malignant tumors (e.g., colon polyps) are non-cancerous but can turn malignant if untreated.
10 Tumor Symptoms You Should Never Ignore
- Unexplained lumps (under skin or in breasts).
- Persistent pain (localized or radiating).
- Sudden weight loss (without dieting).
- Fatigue that doesn’t improve with rest.
- Skin changes (yellowing, dark spots, or sores).
- Bowel/bladder habit changes (blood in stool/urine).
- Neurological issues (seizures, vision loss, headaches).
- Difficulty swallowing or hoarseness.
- Night sweats or recurring fevers.
- Swollen lymph nodes (neck, armpits, groin).
When to See a Doctor: If symptoms last >2 weeks or worsen rapidly.
What Causes Tumors? Risk Factors Explained
- Genetic Mutations: Inherited (e.g., BRCA1 for breast cancer) or acquired (from toxins).
- Environmental Triggers:
- Carcinogens: Tobacco, asbestos, UV radiation.
- Infections: HPV (cervical cancer), Hepatitis B/C (liver cancer).
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, alcohol, sedentary habits.
- Age: 60% of tumors occur in adults over 65.
- Weakened Immunity: HIV/AIDS, organ transplant patients.
How Are Tumors Diagnosed?
- Imaging Tests:
- MRI/CT Scans: Detailed 3D images of soft tissues.
- PET Scans: Detect metabolic activity (cancer vs. benign).
- Biopsy: Removing tissue for lab analysis (definitive diagnosis).
- Blood Tests: Tumor markers (e.g., PSA for prostate cancer).
Pro Tip: Ask about liquid biopsies—a non-invasive blood test detecting tumor DNA.
Modern Tumor Treatments: From Surgery to Immunotherapy
1. Surgery
- Benign Tumors: Often removed for comfort/prevention (e.g., fibroids).
- Malignant Tumors: Tumor resection + margin of healthy tissue.
2. Radiation Therapy
- Targets cancer cells with high-energy beams (e.g., IMRT, proton therapy).
3. Chemotherapy
- Drugs kill fast-growing cells (oral or IV). Side effects: Hair loss, nausea.
4. Immunotherapy
- Boosts the immune system to fight cancer (e.g., Keytruda for melanoma).
5. Targeted Therapy
- Attacks specific mutations (e.g., HER2 inhibitors for breast cancer).
6. Palliative Care
- Manages pain/symptoms for advanced cancers.
Breakthrough Alert: CAR-T cell therapy reprograms immune cells to destroy tumors.
Can Tumors Be Prevented? 6 Science-Backed Tips
- Avoid Carcinogens: Quit smoking, limit alcohol, use sunscreen.
- Vaccinations: HPV vaccine (prevents cervical cancer), Hepatitis B vaccine.
- Screenings: Mammograms (40+), colonoscopies (45+), skin checks.
- Diet: Cruciferous veggies (broccoli), berries, turmeric.
- Exercise: 150 mins/week reduces tumor risk by 20%.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress weakens immunity.
FAQs About Tumors

Q: Are all tumors cancerous?
A: No—benign tumors don’t spread and are rarely life-threatening.
Q: Can tumors go away on their own?
A: Rarely. Some benign tumors (e.g., cysts) may shrink, but most require treatment.
Q: How fast do malignant tumors grow?
A: Varies. Aggressive cancers (e.g., pancreatic) spread in months; others take years.
Q: Is a biopsy painful?
A: Local anesthesia minimizes discomfort. Most report mild pressure, not pain.
Conclusion
Tumors range from harmless to life-threatening, but early detection saves lives. Schedule regular checkups, know your body, and act on unusual symptoms.