Skin cancer affects over 5 million Americans annually, making it the most common form of cancer in the United States. Celebrity advocates like John Cena have brought increased awareness to skin cancer prevention, emphasizing the importance of early detection and sun protection. This comprehensive guide explores evidence-based prevention strategies that can significantly reduce your risk.
What Is Skin Cancer?
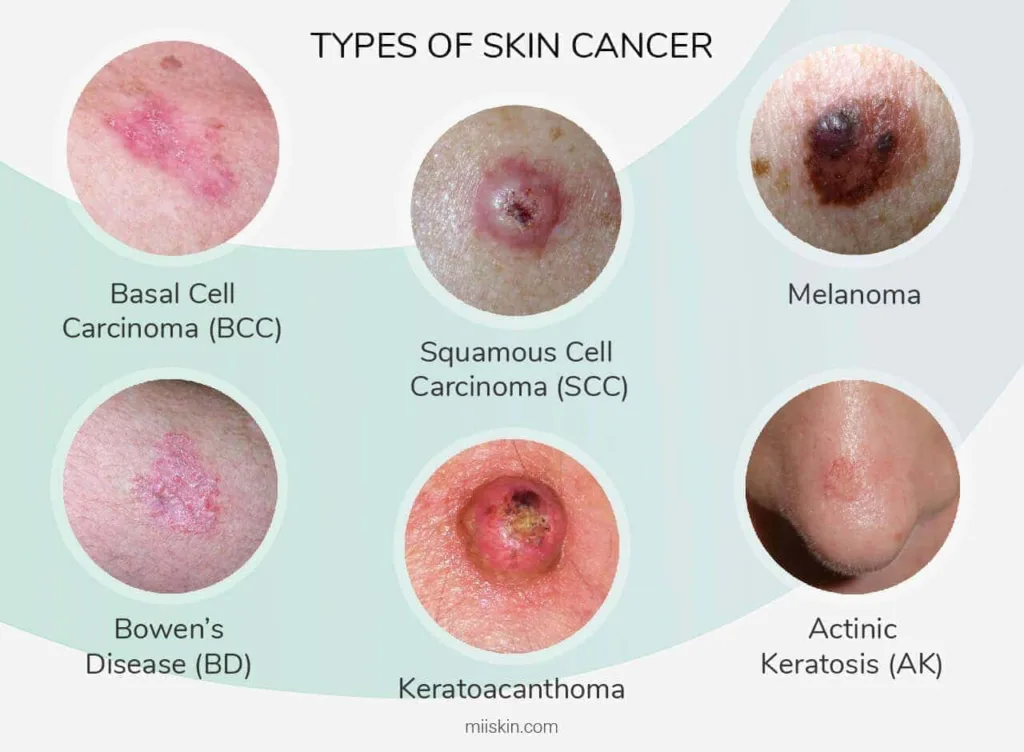
Skin cancer occurs when skin cells grow uncontrollably due to DNA damage, primarily caused by ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds. The three main types are:
- Basal Cell Carcinoma: Most common, rarely spreads
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Can spread if untreated
- Melanoma: Most dangerous, can metastasize quickly
Early detection and prevention are crucial, as skin cancer has a 99% cure rate when caught early.
Celebrity Advocacy Impact: Learning from Public Awareness
John Cena and other celebrities have used their platforms to promote skin cancer awareness, demonstrating that prevention affects everyone regardless of age, skin type, or lifestyle. Their advocacy has helped normalize regular skin checks and sun protection practices, making these health measures more socially acceptable and widely adopted.
Essential Sunscreen Protection Strategies
Choosing the Right Sunscreen
SPF Requirements
- Use broad-spectrum SPF 30 or higher daily
- SPF 50+ for extended outdoor activities
- Water-resistant formulas for swimming or sweating
Application Guidelines
- Apply 1 ounce (2 tablespoons) for full body coverage
- Reapply every 2 hours or after swimming/sweating
- Don’t forget ears, lips, feet, and scalp
Sunscreen Ingredients to Consider
Physical Sunscreens (Zinc oxide, Titanium dioxide)
- Provide immediate protection
- Better for sensitive skin
- Less likely to cause irritation
Chemical Sunscreens (Avobenzone, Octinoxate)
- Absorb into skin for protection
- Often more cosmetically elegant
- May require 15-30 minutes to activate
Comprehensive Prevention Measures

Sun Avoidance Strategies
Peak Hour Protection Avoid direct sun exposure between 10 AM and 4 PM when UV rays are strongest.
Shade Seeking Utilize umbrellas, trees, and covered areas, remembering that UV rays can reflect off water, sand, and concrete.
Protective Clothing and Accessories
UPF-Rated Clothing Choose garments with Ultraviolet Protection Factor (UPF) ratings of 30 or higher.
Wide-Brimmed Hats Select hats with at least 4-inch brims to protect face, neck, and ears.
UV-Blocking Sunglasses Wear sunglasses that block 99-100% of UV-A and UV-B rays to protect the delicate eye area.
Home-Based Prevention and Monitoring
Self-Examination Techniques
Monthly Skin Checks Examine your entire body monthly using the ABCDE method:
- Asymmetry: One half doesn’t match the other
- Border: Irregular, scalloped, or poorly defined edges
- Color: Varies from one area to another
- Diameter: Larger than 6mm (pencil eraser size)
- Evolving: Changes in size, shape, color, or texture
Creating a Skin-Healthy Environment
Indoor UV Protection Use window films or UV-blocking window treatments in homes and vehicles.
Safe Tanning Alternatives Consider sunless tanning products instead of UV tanning beds, which increase melanoma risk by 75%.
Risk Factors and Who Should Be Extra Cautious
High-Risk Individuals
- Fair skin, light hair, and light eyes
- Family history of skin cancer
- History of sunburns or excessive sun exposure
- Weakened immune system
- Age over 50
Occupational Considerations
Outdoor workers, athletes, and frequent travelers need enhanced protection strategies.
Treatment Options and Early Intervention
Professional Treatments
- Surgical excision: Complete removal of cancerous tissue
- Mohs surgery: Precise removal with minimal healthy tissue loss
- Radiation therapy: For cases where surgery isn’t suitable
- Immunotherapy: For advanced melanoma cases
When to Seek Medical Attention
Consult a dermatologist immediately if you notice:
- New growths or changing moles
- Sores that don’t heal within 2-3 weeks
- Unusual bleeding, itching, or pain in skin lesions
Potential Side Effects of Prevention Methods
Sunscreen Considerations
- Skin irritation: Some chemical ingredients may cause reactions
- Vitamin D concerns: Balanced sun exposure or supplements may be needed
- Eye irritation: Avoid getting sunscreen in eyes
Protective Clothing Issues
- Heat retention: Choose breathable, moisture-wicking fabrics
- Comfort: Ensure proper fit to encourage consistent use
How to Avoid Common Prevention Mistakes

Application Errors
Don’t rely on makeup with SPF as your primary protection, and avoid expired sunscreen products.
Coverage Gaps
Remember often-missed areas like between toes, behind ears, and along the hairline.
Weather Misconceptions
UV rays penetrate clouds, so protection is needed even on overcast days.
Indoor Assumptions
Windows don’t block all UV rays, especially UV-A radiation.
Building Sustainable Sun Protection Habits
Daily Routine Integration
Make sunscreen application part of your morning routine, like brushing teeth.
Family Protection Plans
Establish household rules for sun protection and lead by example.
Technology Assistance
Use UV index apps and reminders to stay informed about daily sun intensity levels.
Frequently Asked Questions

Q: How often should I get professional skin cancer screenings?
A: Adults should have annual full-body skin exams by a dermatologist, with more frequent visits if you’re high-risk or have a history of skin cancer.
Q: Can people with darker skin get skin cancer?
A: Yes, while less common, skin cancer can affect all skin types. People with darker skin often develop melanoma in areas with less pigmentation, like palms, soles, and under nails.
Q: Is it safe to use last year’s sunscreen?
A: Sunscreen typically expires after 3 years, but check the expiration date. Expired sunscreen may be less effective and could cause skin irritation.
Q: Do I need sunscreen indoors or on cloudy days?
A: Yes, UV rays can penetrate windows and clouds. Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen daily, regardless of weather or indoor activities near windows.
Q: How much does celebrity advocacy really help with skin cancer awareness?
A: Celebrity advocacy significantly increases public awareness and normalizes prevention behaviors. Studies show that celebrity health campaigns can increase screening rates and protective behaviors by 20-30%.
Q: Can I get enough vitamin D while protecting myself from skin cancer?
A: Yes, you can maintain healthy vitamin D levels through brief sun exposure (10-15 minutes daily), vitamin D supplements, or foods like fatty fish and fortified products while still practicing sun safety.
Conclusion
Skin cancer prevention requires a multi-faceted approach combining proper sunscreen use, protective behaviors, and regular monitoring. Celebrity advocates like John Cena have helped normalize these important health practices, making prevention more accessible and socially acceptable. By implementing comprehensive sun protection strategies and maintaining awareness of your skin’s changes, you can significantly reduce your risk while enjoying outdoor activities safely.
Remember that prevention is always more effective than treatment, and early detection saves lives. Make sun protection a daily habit, not just a summer consideration.
Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and regular skin cancer screenings, especially if you have risk factors or concerning skin changes.








